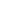
If they send one to eight participants, the fixed cost for the van would be \(\$200\). If they send nine to sixteen students, the fixed cost would be \(\$400\) because they will need two vans. We would consider the relevant wave vs quickbooks range to be between one and eight passengers, and the fixed cost in this range would be \(\$200\). If they exceed the initial relevant range, the fixed costs would increase to \(\$400\) for nine to sixteen passengers.
- To fully understand contribution analysis, you have to be aware of the different cost breakdowns or allocations a company uses.
- This knowledge can be used to drive down fixed costs or increase the contribution margin on product sales, thereby fine-tuning profits.
- This analysis works by allocating direct costs and variable costs and separating them from overhead, also known as fixed costs that are incurred throughout.
- If they send one to eight participants, the fixed cost for the van would be \(\$200\).
- Although the company has less residual profit per unit after all variable costs are incurred, these types of companies may have little to no fixed costs and maybe keep all profit at this point.
- Also known as dollar contribution per unit, the measure indicates how a particular product contributes to the overall profit of the company.
To understand how profitable a business is, many leaders look at profit margin, which measures the total amount by which revenue from sales exceeds costs. To calculate this figure, you start by looking at a traditional income statement and recategorizing all costs as fixed or variable. This is not as straightforward as it sounds, because it’s not always clear which costs fall into each category. Analyzing the contribution margin helps managers make several types of decisions, from whether to add or subtract a product line to how to price a product or service to how to structure sales commissions. Before making any major business decision, you should look at other profit measures as well. If you need to estimate how much of your business’s revenues will be available to cover the fixed expenses after dealing with the variable costs, this calculator is the perfect tool for you.
Contribution measures how much is being contributed to pay Indirect Costs (Overheads) by the units of a particular product that have been produced and sold. For League Recreation’s Product A, a premium baseball, the selling price per unit is $8.00. For example, a company sells 10,000 shoes for total revenue of $500,000, with a cost of goods sold of $250,000 and a shipping and labor expense of $200,000. To illustrate how this form of income statement can be used, contribution margin income statements for Hicks Manufacturing are shown for the months of April and May. For example, assume that the students are going to lease vans from their university’s motor pool to drive to their conference. A university van will hold eight passengers, at a cost of \(\$200\) per van.
Introduction to Business Costs (Revision Presentation)
Sales equals 1 million bottles multiplied by $1.50 each, which comes to $1.5 million. Total variable cost equals $1 per bottle multiplied by the 1 million bottles, which comes to $1 million. The total or gross contribution margin is $1.5 million minus $1 million, which equals $500,000. In the United States, similar labor-saving processes have been developed, such as the ability to order groceries or fast food online and have it ready when the customer arrives. Do these labor-saving processes change the cost structure for the company?
Variable Costs
To see an example of how a firm can use the contribution margin in analyzing operating profit let’s continue to use the bottled drink example from above. Contribution at first contributes towards the fixed overhead and when the fixed overheads are recovered the same contributes towards profit. Gross profit is the dollar difference between https://intuit-payroll.org/ net revenue and cost of goods sold. Gross margin is the percent of each sale that is residual and left over after cost of goods sold is considered. The former is often stated as a whole number, while the latter is usually a percentage. For example, consider a soap manufacturer that previously paid $0.50 per bar for packaging.
The company’s contribution margin of $3.05 will cover fixed costs of $2.33, contributing $0.72 to profits. As you will learn in future chapters, in order for businesses to remain profitable, it is important for managers to understand how to measure and manage fixed and variable costs for decision-making. In this chapter, we begin examining the relationship among sales volume, fixed costs, variable costs, and profit in decision-making.
To resolve bottlenecks, contribution margin can be used to decide which products offered by the business are more profitable and, therefore, more advantageous to produce, given limited resources. Preference is given to products that provide a high contribution margin. Unit contribution can also be calculated using contribution margin if the number of units sold is known.
Learn How NetSuite Can Streamline Your Business
When allocating scarce resources, the contribution margin will help them focus on those products or services with the highest margin, thereby maximizing profits. Contribution margin is not intended to be an all-encompassing measure of a company’s profitability. However, contribution margin can be used to examine variable production costs. Contribution margin can also be used to evaluate the profitability of an item and calculate how to improve its profitability, either by reducing variable production costs or by increasing the item’s price. For an example of contribution margin, take Company XYZ, which receives $10,000 in revenue for each widget it produces, while variable costs for the widget is $6,000. The contribution margin is calculated by subtracting variable costs from revenue, then dividing the result by revenue, or (revenue – variable costs) / revenue.
The calculation of the metric is relatively straightforward, as the formula consists of revenue minus variable costs. You can also mention contribution margin in the skills section of your resume. Since contribution margins are one way to measure profitability, you could list that you are skilled in measuring profitability using various methods, such as contribution and profit margins.
Should the company enter into an agreement to pay $500 for all packaging for all bars manufactured this month. Gross margin would report both types of costs the same (include it in its calculation), while contribution margin would consider these costs differently. Most often, a company will analyze gross margin on a company-wide basis. This is how gross margin is communicated on a company’s set of financial reports, and gross margin may be more difficult to analyze on a per-unit basis.
Business
It’s the study and assessment of how direct and variable costs affect net income. The more revenue available after variable costs are covered, the better, especially considering how expensive fixed expenses like rent and salaries can be. At the very least, a product must have a positive contribution margin to be worth producing. So, even if the product isn’t that profitable, the company can break even as long as the margin is high enough to cover fixed expenses. Additionally, companies can improve contribution margins by adjusting production costs and making processes more efficient.
In particular, the use-case of the CM metric tends to be most practical for companies to set prices on their products and services appropriately to maximize their revenue growth and profitability. Thus, you need to make sure that the contribution margin covers your fixed cost and the target income you want to achieve. Contribution margin calculation is one of the important methods to evaluate, manage, and plan your company’s profitability. Further, the contribution margin formula provides results that help you in taking short-term decisions. Calculating the contribution margin for each product is one solution to business and accounting problems arising from not doing enough financial analysis.
What is Contribution?
Contribution may also be considered from another standpoint, i.e., wherefrom does it come? [Sales – Variable Cost – Contribution Equation] and how the same is applied [Profit – Fixed Overhead – Contribution Equation]. Contribution analysis helps compare how individual products are profitable to the company and is easy to use. This is because fee-for-service hospitals have a positive contribution margin for almost all elective cases mostly due to a large percentage of OR costs being fixed.
Contribution-Costing Technique avoids all this mess with the allocations of Indirect Costs (Overheads) into each particular product. This link between contribution to Indirect Costs (Overheads), and then to profit, is a crucial one. We can clearly see the role of contribution costing in pricing decisions. When the amount of contribution is lower than Indirect Costs (Overheads), the loss will be made. It means that products contribute less than enough to cover all Indirect Costs (Overheads), and all Direct Costs of course.
To demonstrate this principle, let’s consider the costs and revenues of Hicks Manufacturing, a small company that manufactures and sells birdbaths to specialty retailers. Direct materials are often typical variable costs, because you normally use more direct materials when you produce more items. In our example, if the students sold \(100\) shirts, assuming an individual variable cost per shirt of \(\$10\), the total variable costs would be \(\$1,000\) (\(100 × \$10\)). If they sold \(250\) shirts, again assuming an individual variable cost per shirt of \(\$10\), then the total variable costs would \(\$2,500 (250 × \$10)\). Gross margin is synonymous with gross profit margin and includes only revenue and direct production costs.
Alternatively, contribution margin is often more accessible and useful on a per-unit or per-product basis. A company will be more interested in knowing how much profit for each unit can be used to cover fixed costs as this will directly impact what product lines are kept. This means that 90% of the total sales revenue from each unit sold is available to cover fixed costs. For every pair of wireless headphones sold, the company makes $58.90, which it will use to cover fixed costs and, ideally, gain a profit. Another way to look at this is to consider the contribution margin ratio, though.